---
title: "Lecture 12: Introduction to Git and GitHub"
date: "2025-02-05"
execute:
eval: false
echo: true
warning: false
output-location: default
code-annotations: below
format:
html:
code-tools: true
code-line-numbers: false
code-fold: false
number-offset: 0
---
# Introduction to Git and GitHub
## What is Git?
- A distributed version control system
- Tracks changes in files
- Allows multiple users to work on the same project
------------------------------------------------------------------------
## Why Use Git?
- **Version Control**: Keep track of changes made to code or documents
- **Collaboration**: Allow multiple developers to work on the same codebase
- **Backup**: Keep a backup of previous versions of your project
------------------------------------------------------------------------
## What is GitHub?
- A platform for hosting Git repositories
- Enables collaboration with others on code-based projects
- Provides cloud storage for your code
------------------------------------------------------------------------
## Git vs. GitHub
- **Git**: A tool for managing versions of your code locally
- **GitHub**: A web-based service for hosting Git repositories and collaboration
------------------------------------------------------------------------
## Setting Up Git
1. Install Git on your computer
- [Git Download](https://git-scm.com/downloads)
2. Configure Git in your terminal
``` bash
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
git config --global user.email "youremail@example.com"
```
3. Install GitHub Desktop
- [GitHub Desktop Download](https://github.com/apps/desktop)
```{=html}
<blockquote class="reddit-embed-bq" data-embed-showtitle="true" data-embed-context="1" data-embed-depth="2" data-embed-theme="dark" data-embed-showusername="false" data-embed-height="296"><a href="https://www.reddit.com/r/git/comments/msznyy/comment/guws2du/">Comment</a><br> by<a href="https://www.reddit.com/user/Electronic_Ad2207/">u/Electronic_Ad2207</a> from discussion<a href="https://www.reddit.com/r/git/comments/msznyy/is_git_necessary_when_theres_github_desktop/"></a><br> in<a href="https://www.reddit.com/r/git/">git</a></blockquote><script async="" src="https://embed.reddit.com/widgets.js" charset="UTF-8"></script>
<blockquote class="reddit-embed-bq" data-embed-theme="dark" data-embed-showusername="false" data-embed-height="412"><a href="https://www.reddit.com/r/git/comments/msznyy/comment/guwm8x3/">Comment</a><br> by<a href="https://www.reddit.com/user/Electronic_Ad2207/">u/Electronic_Ad2207</a> from discussion<a href="https://www.reddit.com/r/git/comments/msznyy/is_git_necessary_when_theres_github_desktop/"></a><br> in<a href="https://www.reddit.com/r/git/">git</a></blockquote><script async="" src="https://embed.reddit.com/widgets.js" charset="UTF-8"></script>
```
------------------------------------------------------------------------
## Basic Git Commands
- `git init`: Initialize a new Git repository
- `git add <file>`: Stage changes for commit
- `git commit -m "message"`: Save changes with a commit message
- `git status`: Check the status of your files
- `git log`: View commit history
# Git Terminal
## Creating a GitHub Repository
1. Go to [GitHub](https://github.com).
2. Click on the **+** icon at the top right corner and select **New repository**.
3. Name your repository and choose whether it will be **public** or **private**.
4. Click **Create repository**.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
## Cloning the Repository to Your Local Machine
Once the repository is created on GitHub, follow these steps to clone it to your local machine.
1. Copy the repository URL from GitHub.
2. In your terminal, type:
``` bash
git clone https://github.com/yourusername/yourrepository.git
```
3. Navigate into the repository:
``` bash
cd yourrepository
```
------------------------------------------------------------------------
## Modify Files Locally
1. Create a new file or modify an existing one. Example: Create a file `hello.txt` with the content:
``` txt
Hello, GitHub! This is my first file.
```
2. Check the status of the changes:
``` bash
git status
```
------------------------------------------------------------------------
## Staging Changes
After modifying the files, you need to stage the changes before committing them.
1. Stage the file using the `git add` command:
``` bash
git add hello.txt
```
2. Check the status again to confirm the file is staged:
``` bash
git status
```
------------------------------------------------------------------------
## Committing Changes
1. Commit the staged changes with a descriptive message:
``` bash
git commit -m "Add hello.txt with initial content"
```
2. View the commit history:
``` bash
git log
```
------------------------------------------------------------------------
## Pushing Changes to GitHub
Now that the changes are committed locally, you can push them to GitHub.
1. Push the changes to the GitHub repository:
``` bash
git push origin main
```
2. Check the repository on GitHub, and you should see the file `hello.txt` uploaded.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
## Modifying Existing Files
1. Modify an existing file (e.g., `hello.txt`).
2. Stage the changes:
``` bash
git add hello.txt
```
3. Commit the changes with a message:
``` bash
git commit -m "Update hello.txt with a new message"
```
4. Push the changes to GitHub:
``` bash
git push origin main
```
------------------------------------------------------------------------
## Branching and Merging
1. Create a new branch:
``` bash
git branch new-feature
git checkout new-feature
```
2. Make some changes in a file (e.g., update `hello.txt`).
3. Stage and commit those changes:
``` bash
git add hello.txt
git commit -m "Add a new feature"
```
4. Merge the `new-feature` branch back to `main`:
``` bash
git checkout main
git merge new-feature
```
5. Push the merged changes to GitHub:
``` bash
git push origin main
```
------------------------------------------------------------------------
## Collaborative Workflow on GitHub
1. Fork a repository on GitHub.
2. Clone the forked repository to your local machine:
``` bash
git clone https://github.com/yourusername/forked-repository.git
```
3. Create a new branch:
``` bash
git branch my-branch
git checkout my-branch
```
4. Make changes, commit them, and push them to GitHub:
``` bash
git add .
git commit -m "Describe the changes"
git push origin my-branch
```
5. Create a [pull request](https://docs.github.com/en/pull-requests/collaborating-with-pull-requests/proposing-changes-to-your-work-with-pull-requests/about-pull-requests) to merge your changes into the original repository.
1. [Tutorial of creating a pull request](https://docs.github.com/en/pull-requests/collaborating-with-pull-requests/proposing-changes-to-your-work-with-pull-requests/creating-a-pull-request?tool=desktop)
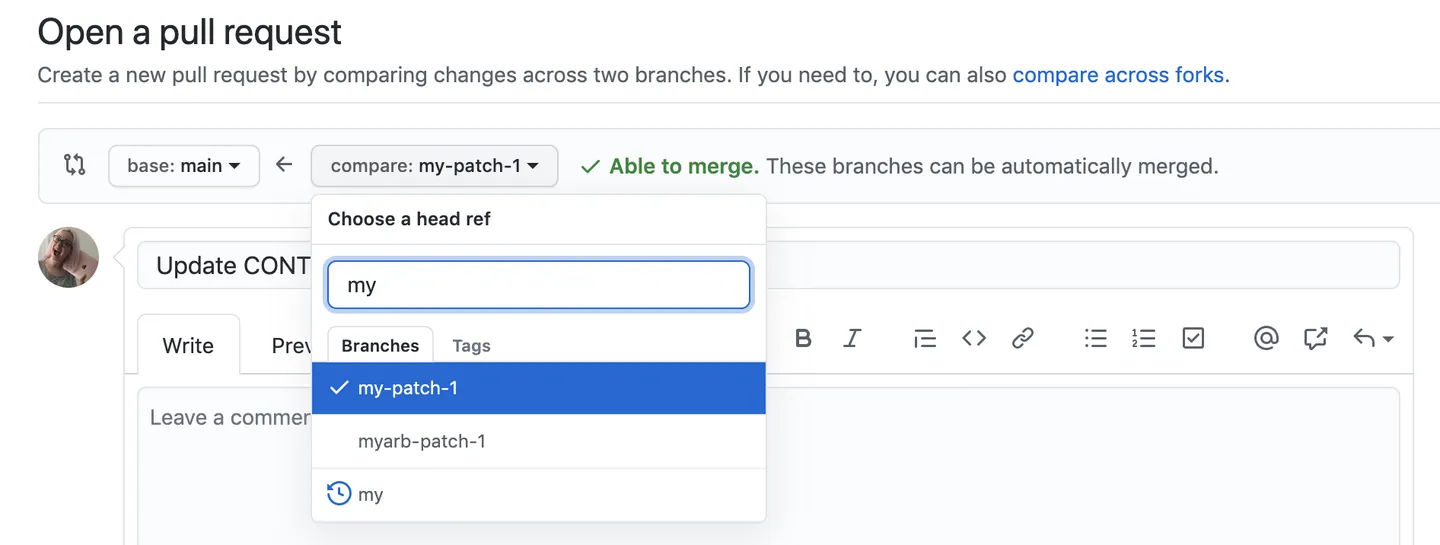
------------------------------------------------------------------------
## A More user-friendly method - GitHub Desktop
```{r}
#| eval: true
#| echo: false
htmltools::tags$iframe(
src = "https://www.youtube.com/embed/CAwStH0ay-M?si=Iie97MNxKGD1NhsR",
scrolling = "no",
seamless = "seamless",
frameborder = "0",
width="100%",
height="769"
)
```
------------------------------------------------------------------------
## GitHub Desktop: Commit Existing Folder
```{r}
#| eval: true
#| echo: false
htmltools::tags$iframe(
src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/unoUc1LNFtY?si=8Ck-8dMeVCujo_l-",
scrolling = "no",
seamless = "seamless",
frameborder = "0",
width="100%",
height="769"
)
```
## Example: Create a new github repository
- You start with a new project
```{r}
#| eval: true
#| echo: false
htmltools::tags$iframe(
src = "https://www.youtube.com/embed/nMvNe3PdO_M?si=Xza9Ybp_BjJMgAZz",
scrolling = "no",
seamless = "seamless",
frameborder = "0",
width="100%",
height="769"
)
```
### Steps for Students to Follow:
1. **Create a new GitHub repository**.
2. **Clone the repository** to their local machine using `git clone`.
3. **Add the `README.md`** file into the repository
4. **Stage, commit**, and **push** the changes back to GitHub.
# Now you prepared all skills for R project
## TidyTuesday Project
Tidytuesday is a weekly social data project that provide a dataset every Tuesday for data scientists to visualize, dashboard, develop shiny app (["tidytuesday GitHub"](https://github.com/rfordatascience/tidytuesday)).
::: rmdquote
- Data is posted to social media every Monday morning.
- Explore the data, watching out for interesting relationships.
- Create a visualization, a model, a Quarto report, a shiny app, or some other piece of data-science-related output, using R, Python, or another programming language.
- Share your output and the code used to generate it on social media with the #TidyTuesday hashtag.
:::
## Today Let's Play with the data
**Project Plan**
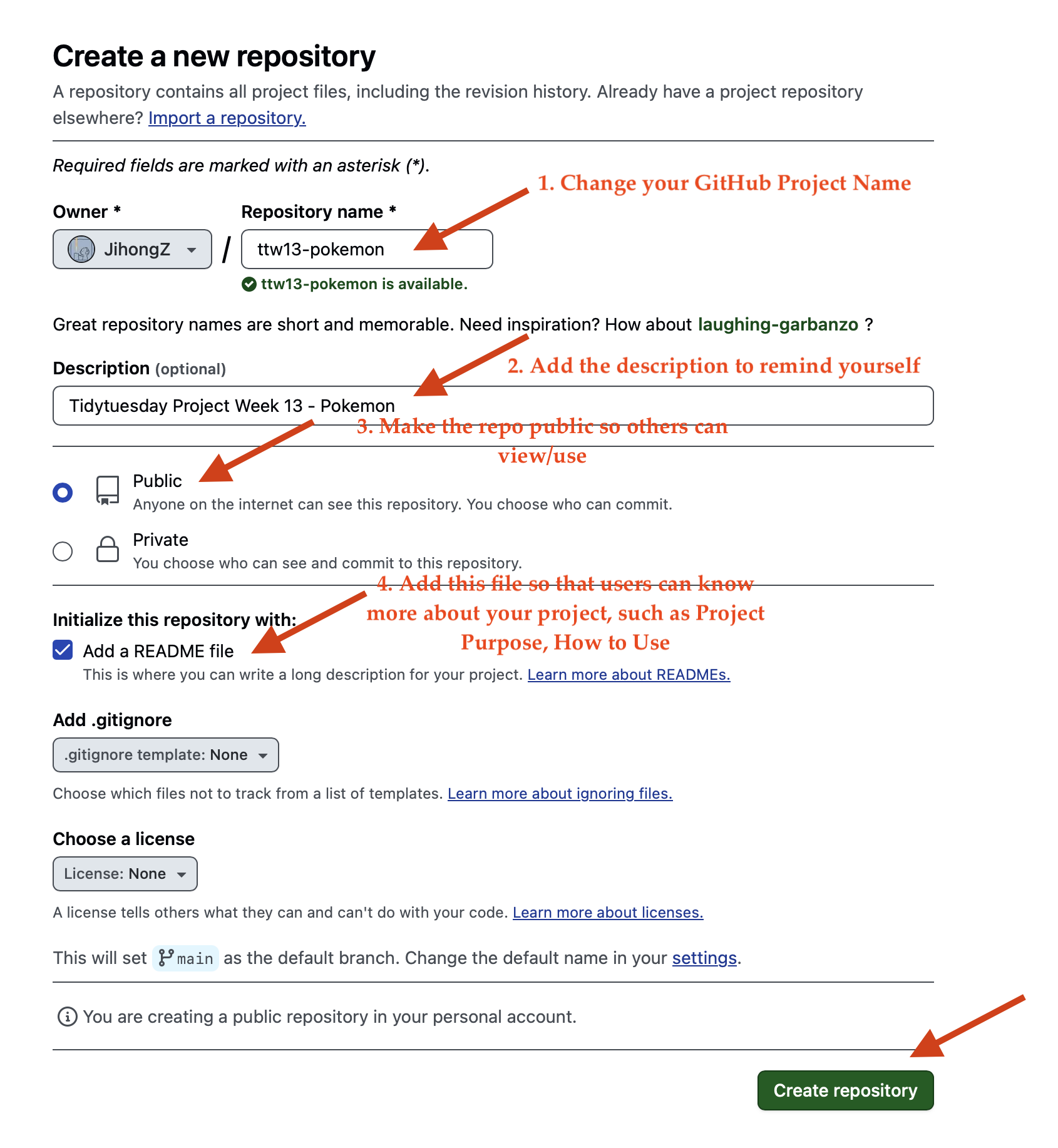
- Step 1: Create a new Git Repo with the name `ttw13-pokemon`
- Step 2: Pull the repo into local
- Step 3: Create a R Project using Rstudio
- Step 4: Authoring: `.R` file to store functions and `.qmd` file to report your results.
- Step 5: Push your local changes into GitHub for others to review.

------------------------------------------------------------------------
### Step 1: Create a new repository
::: panel-tabset
#### Creation
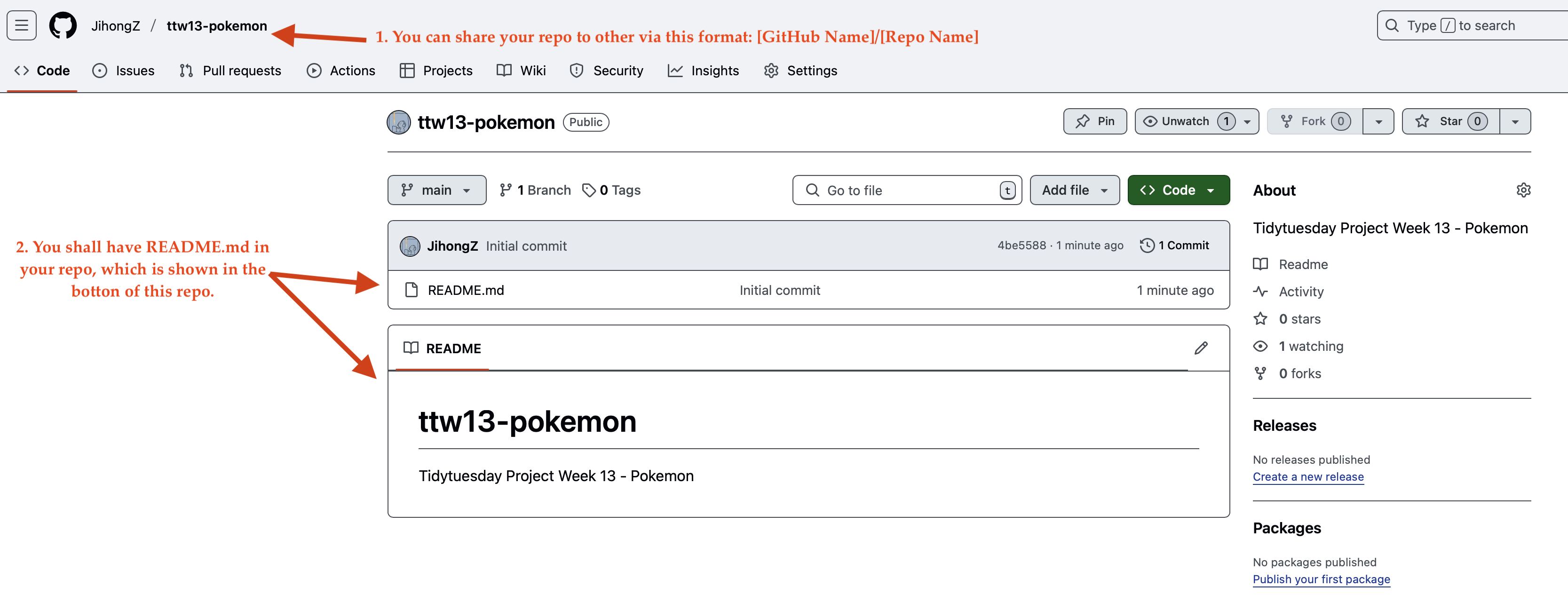
#### Screenshot
:::
### Step 2: Pull the Repo to the Local
::: panel-tabset
#### Step 2.1
Open up GitHub Desktop, Click `Current Repository` \> `Add` \> `Clone Repositoty`.
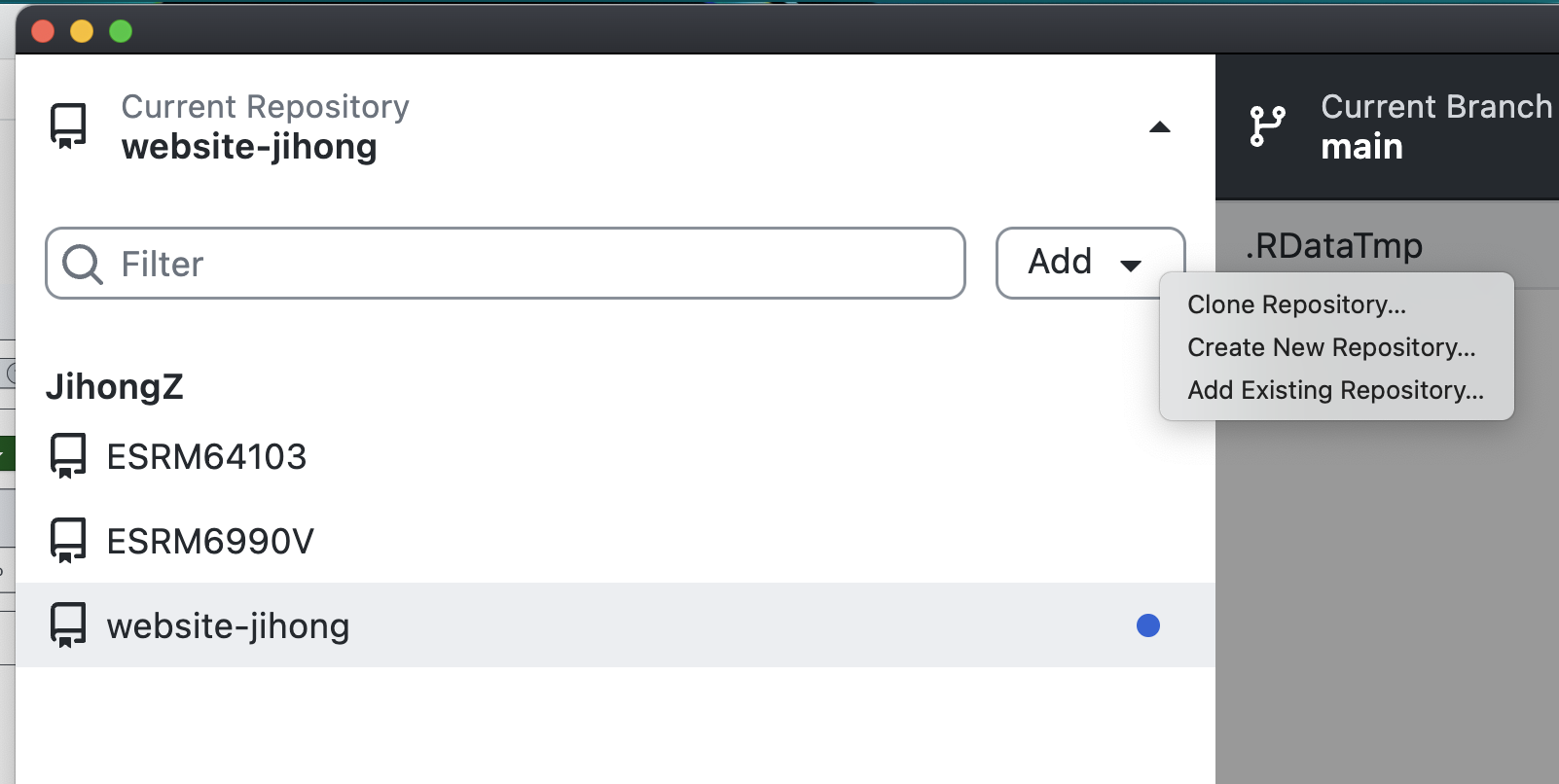
#### Step 2.2
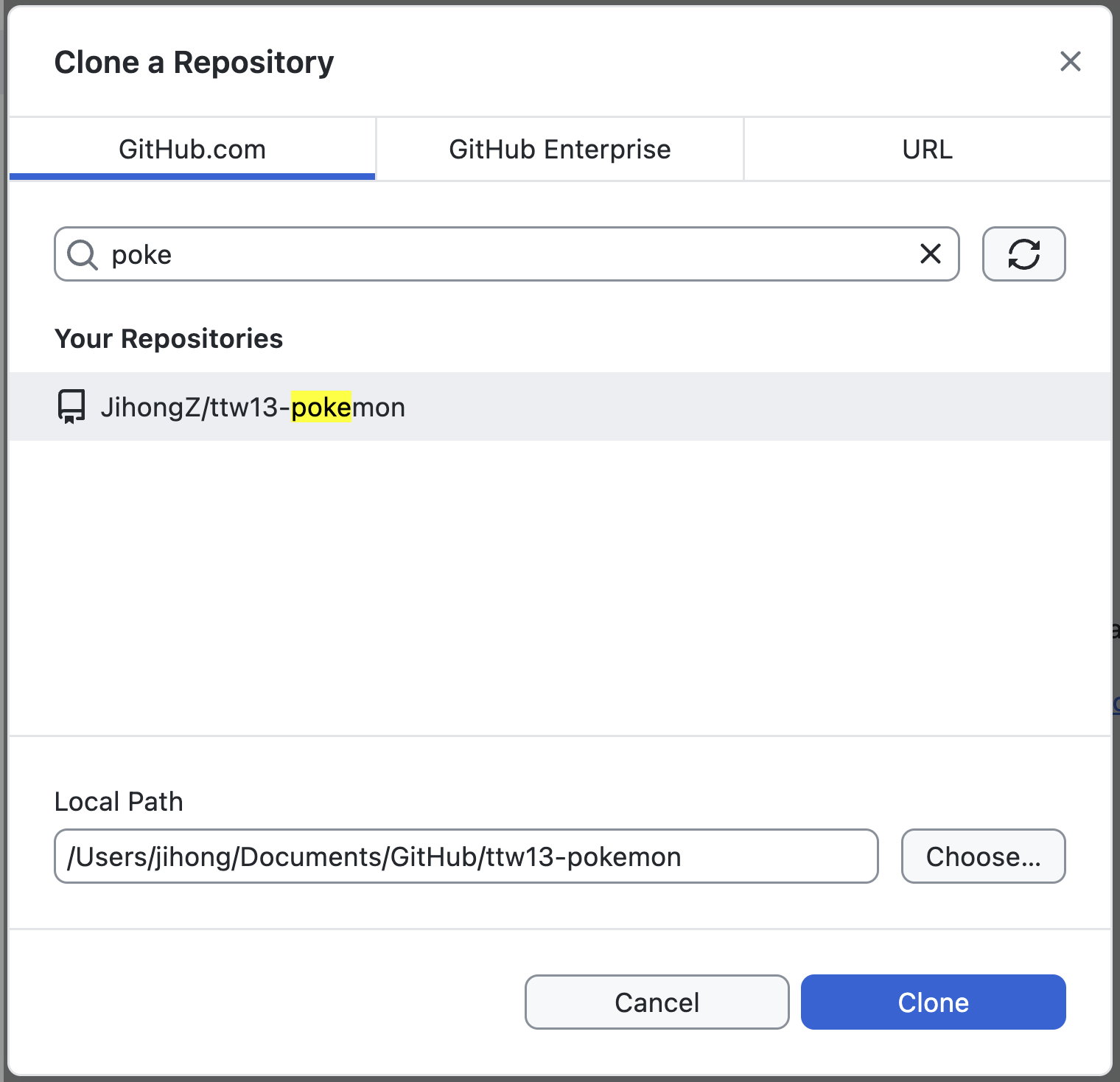
In the pop-up window, search `poke`, then your Repository just created will show up. Click `Choose` to change the `Local Path` where you want to store your project, then click `Clone`.
#### Step 2.3
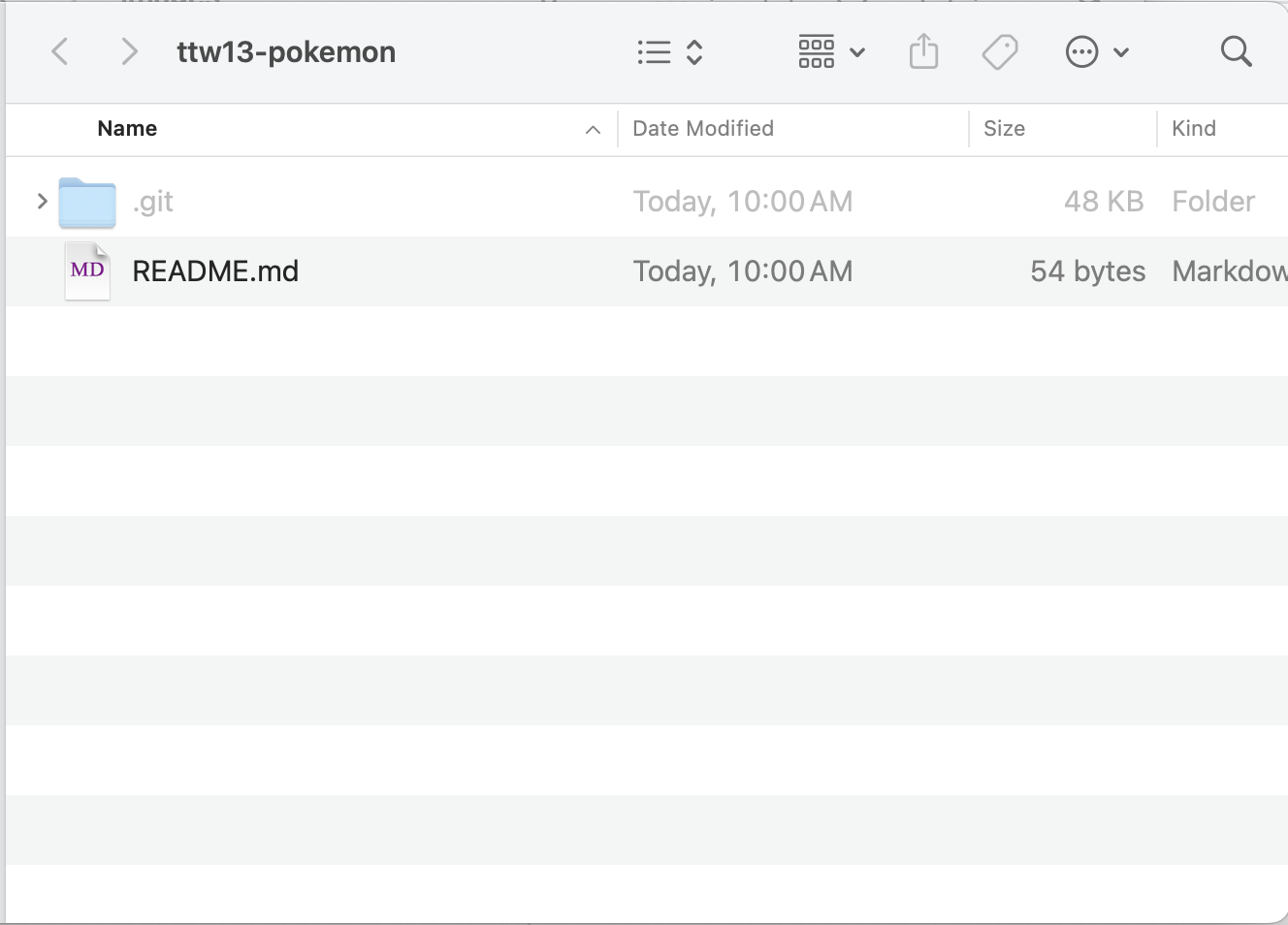
Open you File Management, you shall see a folder named `ttw13-pokemon`.
:::
### Step 3: Create R Project
::: panel-tabset
#### Step 3.1
#### Step 3.2
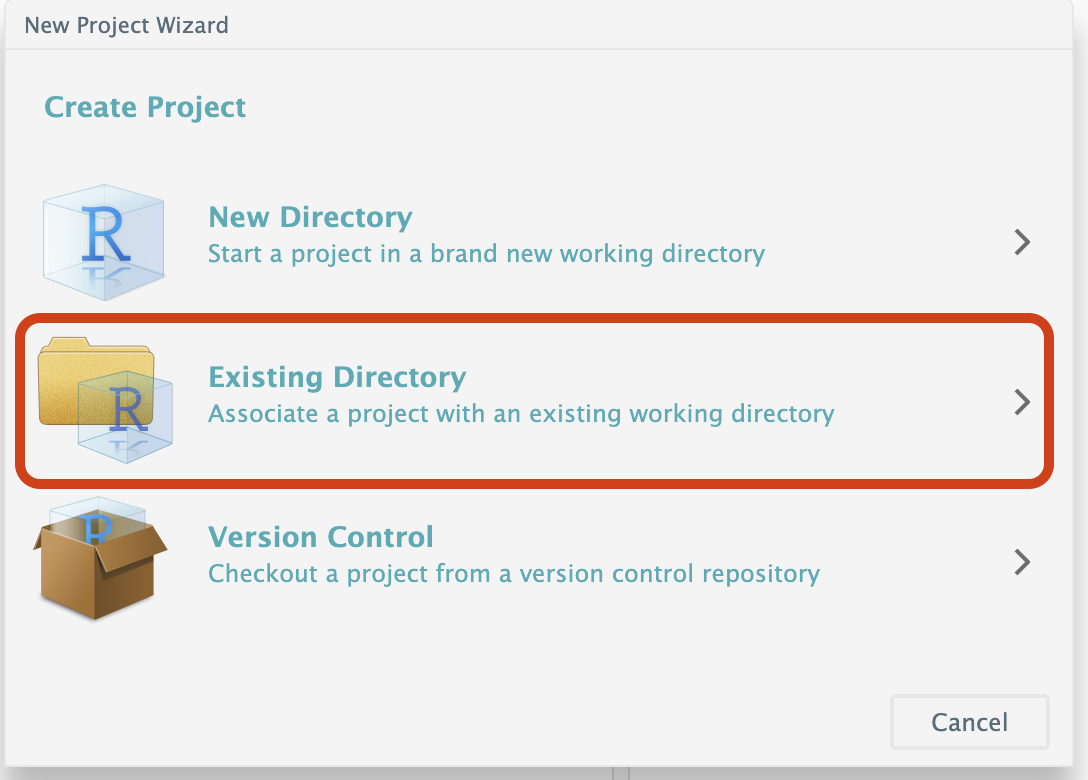
#### Step 3.3
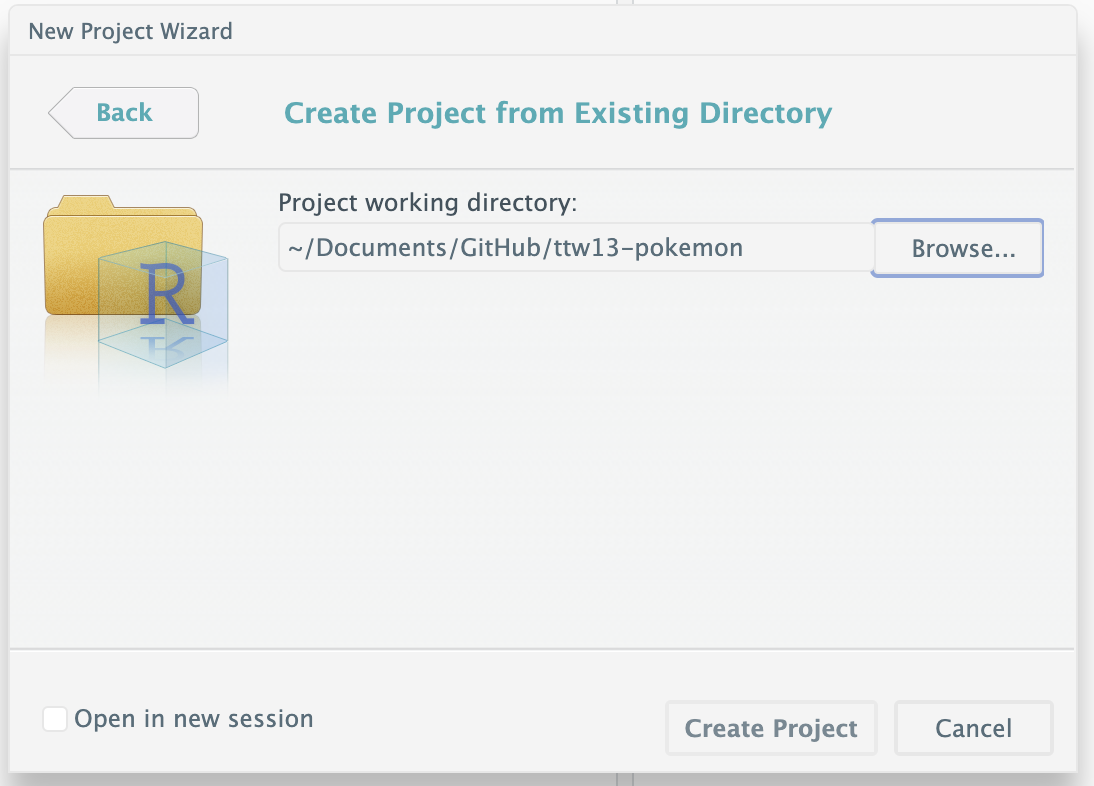
#### Step 3.4
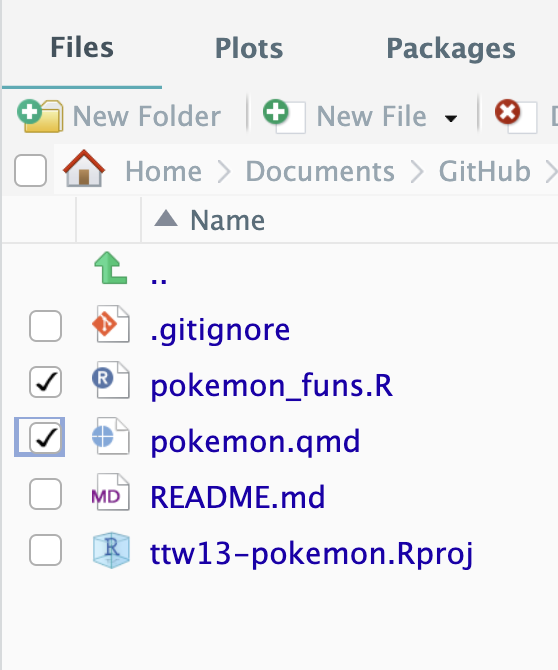
Create a Quarto Document called `pokemon`, and a R file called `pokemon_funs`.
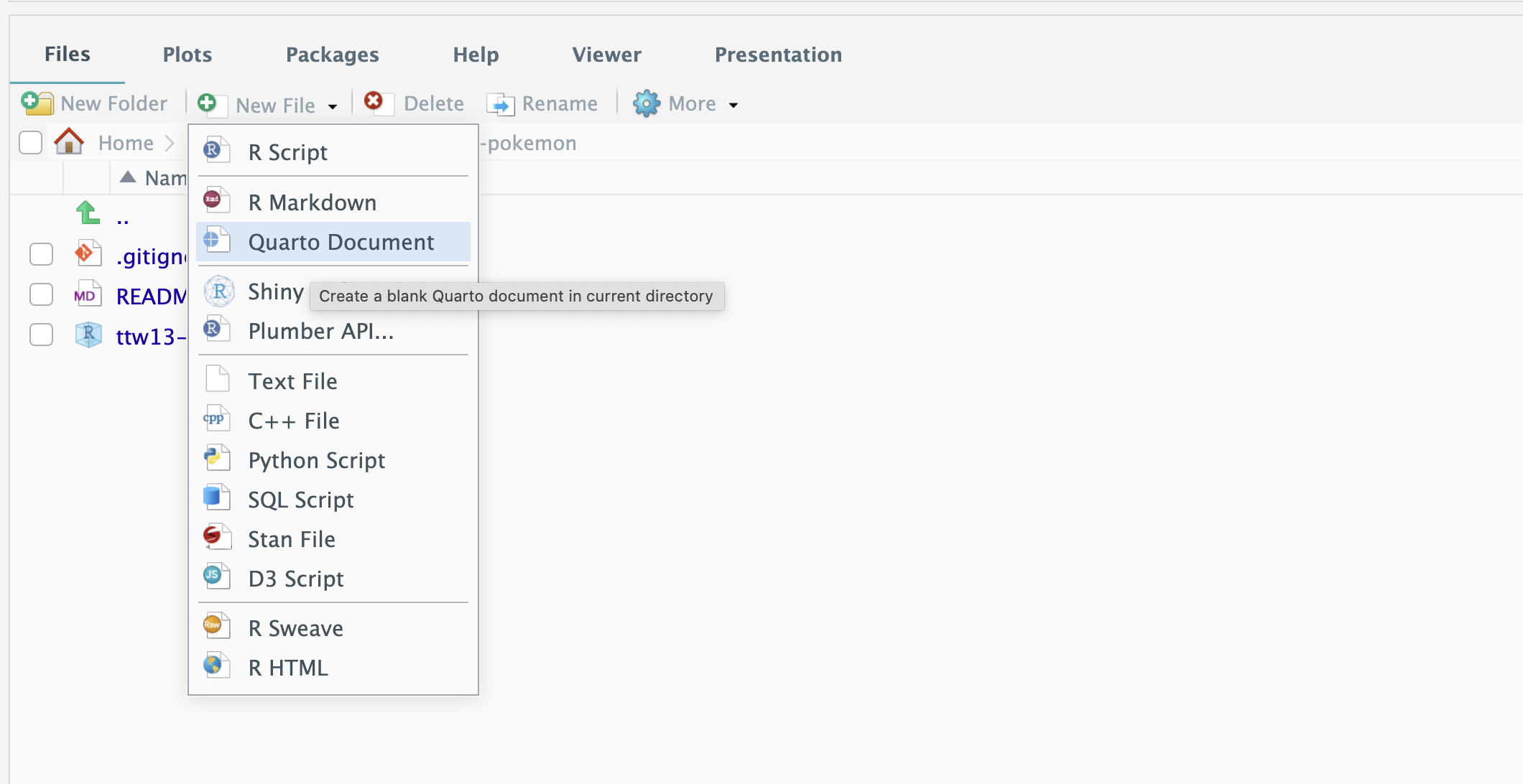
#### Step 3.5
:::
### Step 4: Authoring Quarto and R file
::: panel-tabset
#### Step 4.1
Open up your `pokemon.qmd` file, in the begining of your file, replace the YAML with the followings:
``` yaml
---
title: "Pokemon Data Visualization and Analysis with R"
author: "Jihong Zhang"
date: "2025-04-10"
format: pdf
---
```
#### Step 4.2
Still in `pokemon.qmd` file, cope and paste the following markdown text after the YAML header:
``` markdown
# Motivation
Pokemon is a global icon. It is a TV series that expanded into video games, Pokemon cards/collectibles, and merchandise that made it into a multimillion dollar franchise. Growing up, Pokemon was one of my favorite shows and to this day, it remains one of the fondest memories from my childhood.
# Research Question
Before I begin my project, I should know what I am doing and how to do it. This quarter, I am in my first *Introduction to R* course so my project directly applies the course material. I utilized my lecture notes to learn the technicalities of coding it and the mathematics behind each line I wrote.
After doing my research, I took this approach to solve my own problem: **Could I predict battle outcomes?**
My report is organized into the following section:
1. Loading the Data Set
2. Data Visualization
3. Linear Regression.
```
#### Step 4.3
Click button, do you see a PDF file in the `Viewer` panel?
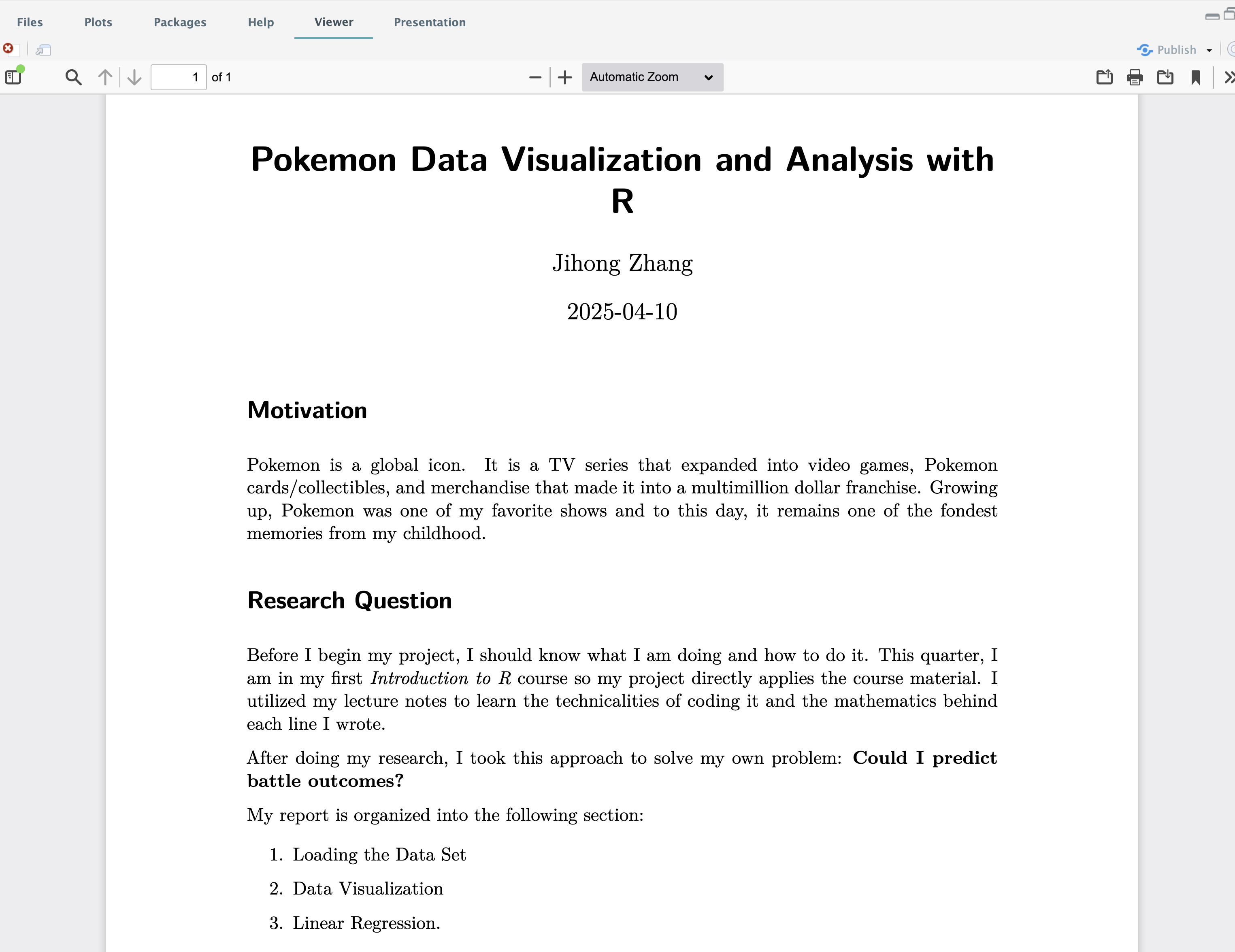
#### Step 4.4
Open up `pokemon_funs.R`, write up and test your R code including data importing, data visualization and modeling code.
Check the Tidytuesday's Document – [Pokemon dataset](https://github.com/rfordatascience/tidytuesday/blob/main/data/2025/2025-04-01/readme.md) to know more details about the sampled data.
As an example, copy and paste the following code.
```{r filename="pokemon_funs.R"}
#| eval: false
# Using R
# Option 1: tidytuesdayR R package
## install.packages("tidytuesdayR")
if( !require(GGally)){
install.packages("GGally")
}
if( !require(tidyverse)){
install.packages("tidyverse")
}
data_url <- 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rfordatascience/tidytuesday/main/data/2025/2025-04-01/pokemon_df.csv'
pokemon <- readr::read_csv(data_url, col_select = c("id", "pokemon", "type_1", "type_2", "hp", "attack", "defense", "special_attack", "special_defense", "speed"))
NewNames <- c('Number', 'Names', 'Type1', 'Type2', 'HP', 'Attack', 'Defense', 'SpAttack', 'SpDefense', 'Speed')
names(pokemon) <- NewNames
cols_to_check <- c("HP", "Attack", "Defense", "SpAttack", "SpDefense", "Speed")
pokemon[, cols_to_check]
fig1 <- ggplot(data=pokemon, mapping=aes(x=Attack, y=Defense, color=Type1))+
geom_boxplot()+
coord_flip()
fig2 <- ggpairs(pokemon, columns = 5:10)
## Linear regression
model1= lm(HP ~ Speed + Attack + Defense + SpAttack + SpDefense, data=pokemon)
tbl1 <- summary(model1)$coefficients
```
#### Step 4.5
After you are satisfied with your data analysis results, write up your Quarto markdown to combine your interpretion and computational results togethor.
As one example, copy the following text and append it to the end of your Quarto file --- `pokemon.qmd`.
```{r, filename="pokemon.qmd"}
#| eval: false
## Data Visualization
Data visualization is a powerful tool. @fig-boxplot shows the characteristics by their Types.
#| message: false
#| echo: false
#| fig-cap: "Boxplot of denfense and attack by their types"
#| label: fig-boxplot
source("pokemon_funs.R")
fig1
Second, I check out the relationships among six dimensions of information of Pokemon using pairwise scatterplot. As shown in @fig-scatter, I did not see clear relationships.
#| message: false
#| echo: false
#| fig-cap: "Pairwise scatterplot"
#| label: fig-scatter
fig2
## Linar Regression Results
#| echo: false
#| label: tbl-regression
#| tbl-cap: "Linear regression of six indices on HP"
kableExtra::kable(tbl1)
As @tbl-regression shows, *Speed* and *Defense* have negative effects on *HP*, while *Attack* has positive effect on Pokemon's HP. *Defense* has no significant relationship with *HP*.
## Conclusion
With this project, I achieved a lot of firsts. It was the first time that I worked with such a large dataset. Not only were there 800 observations, but there were also 12 different variables. This meant I had a lot to play around with and explore, but also there was room for a lot of error.
It was also the first time I have worked with multiple linear regression. I am accustomed to performing linear regression analysis on the relationship between two variables, so working with eight was a new challenge.
```
#### Step 4.6
Update your `README.md` file to illustrate your purpose and how to use your repo.
As an example:
``` markdown
# ttw13-pokemon
Tidytuesday Project Week 13 - Pokemon
# Introduction
I downloaded the Pokemon. Visualized the data to understanding the relationships among HP and other indices.
# File Structure
You can open `pokemon.qmd` to see the report. Alternatively, You can check `pokemon.pdf`.
```
:::
### Step 5: Push your local changes into GitHub
::: panel-tabset
#### Step 5.1
Go back to GitHub Desktop, you will see changes in files.
Add commit messages at the bottom left — "Add .qmd and .R into repo". Click `Commit to main`.
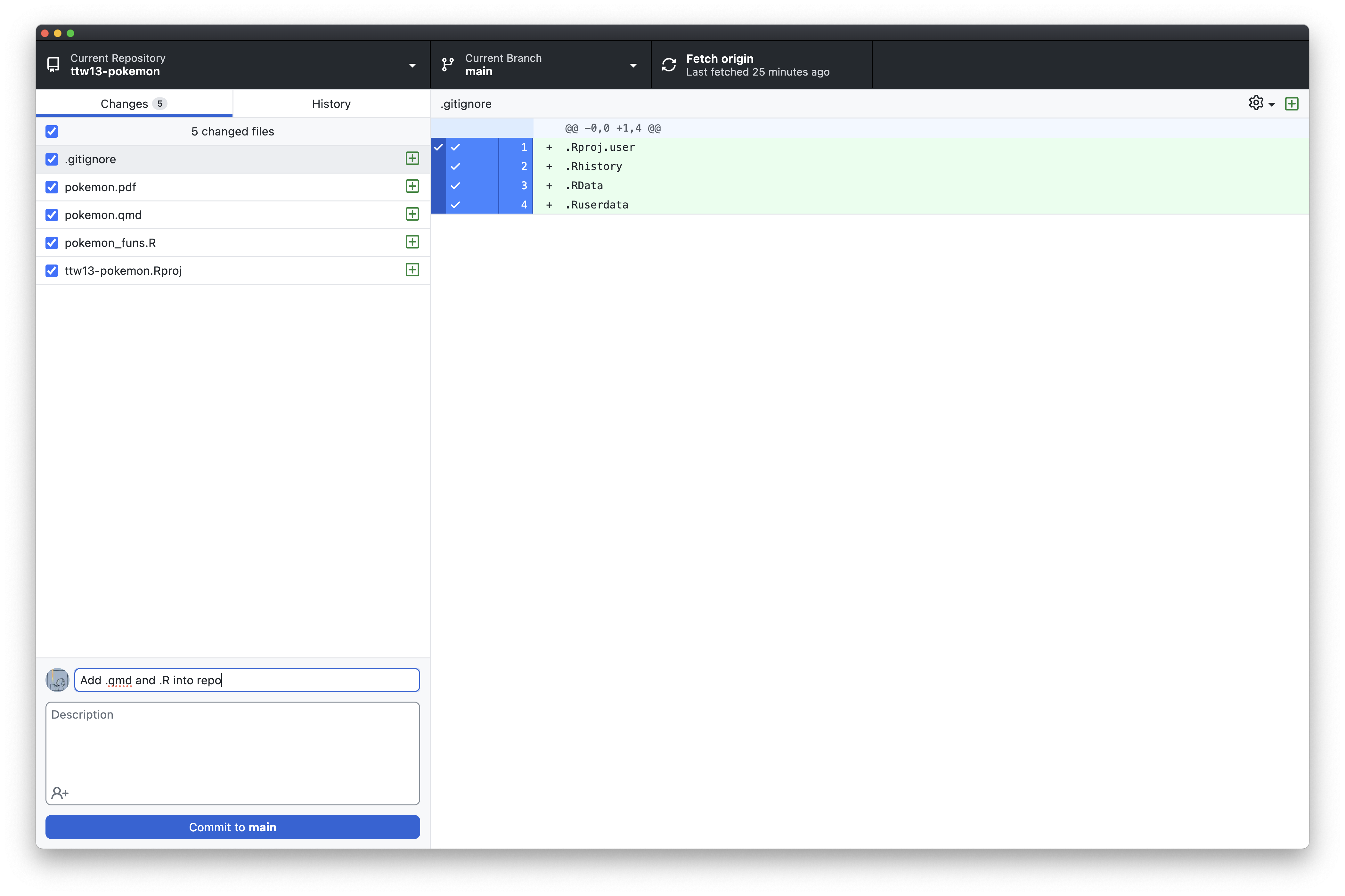
#### Step 5.2
Click `Push origin` to push it to the GitHub
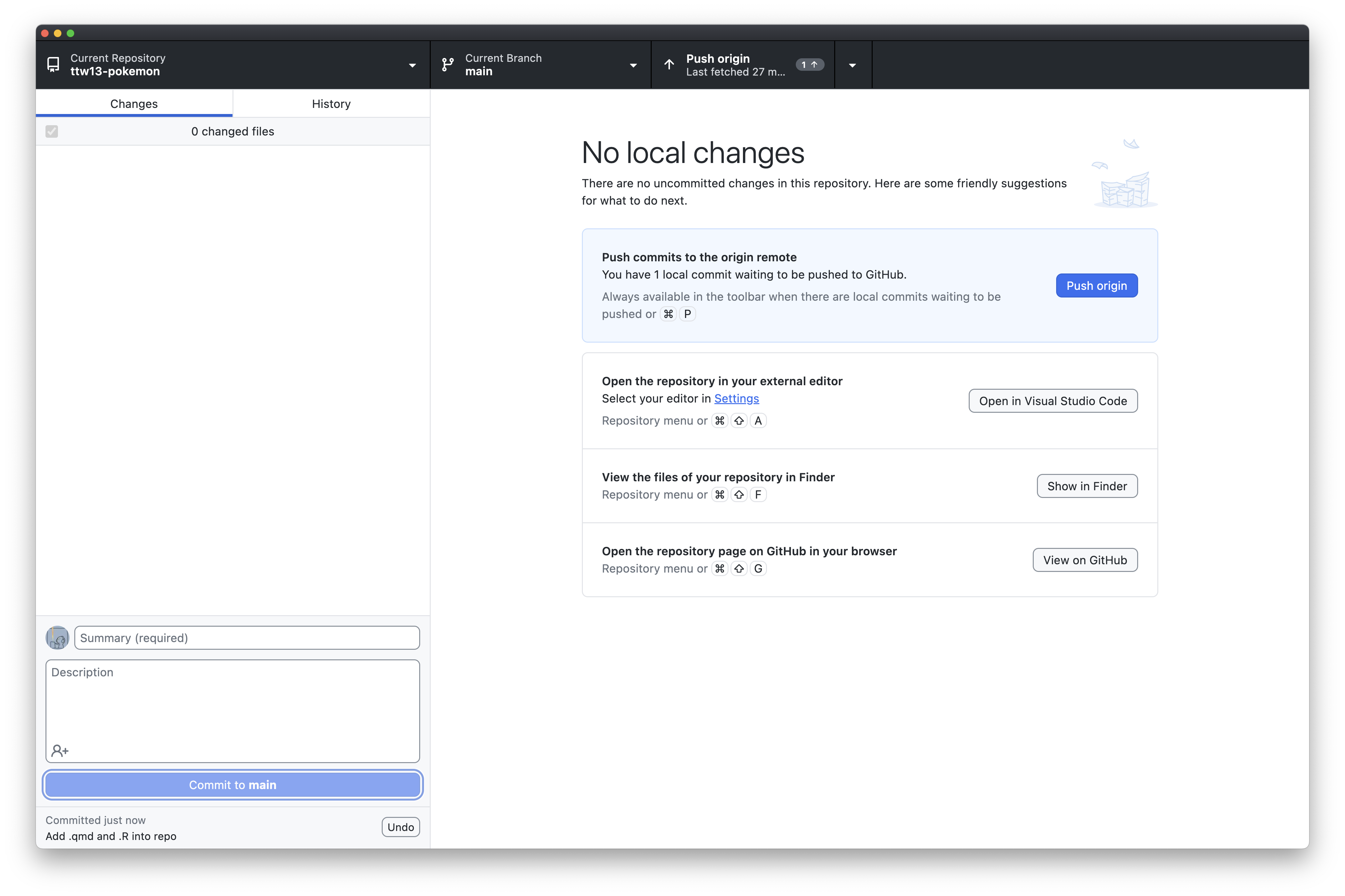
#### Step 5.3
You should see the updated GitHub repo including changed files and documents.
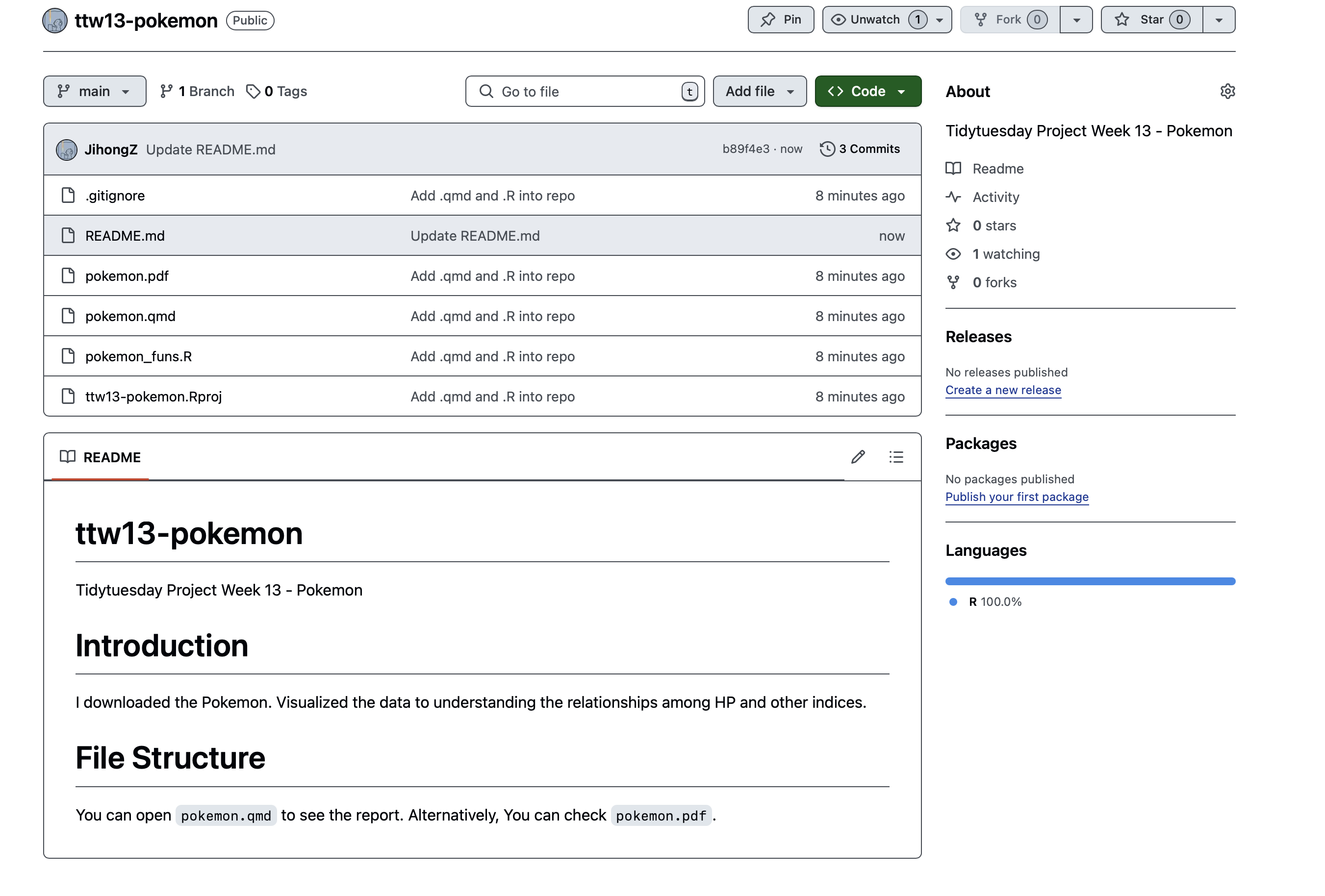
:::
## Conclusion
- Git and GitHub are essential tools for version control and collaboration.
- Git manages local changes, while GitHub enables collaboration in the cloud.
- Start using Git and GitHub for better project management and teamwork!
------------------------------------------------------------------------
## Questions?
Feel free to ask any questions or explore Git and GitHub further!













 button, do you see a PDF file in the
button, do you see a PDF file in the 


